

So, associative arrays can be used in place of a numerically indexed array which reference the items in an array by name instead of a number. The array elements can be tracked easily by the predefined indexing, but this requires a large amount of memory space to remember the exact numbering of the item. The foreach loop work in a proper way with list() and each() constructs also. Unlike for loop, the foreach does not require any initialization and termination expressions.
To make the language more convenient for the programmers, the developers of PHP provided a loop structure specifically designed for the arrays, since the basic loop is not capable of performing operations with an array. The foreach loop is quite different from the for a loop as it permits the iteration of the elements in an array.
PHP ARRAY LENGTH LOOP CODE
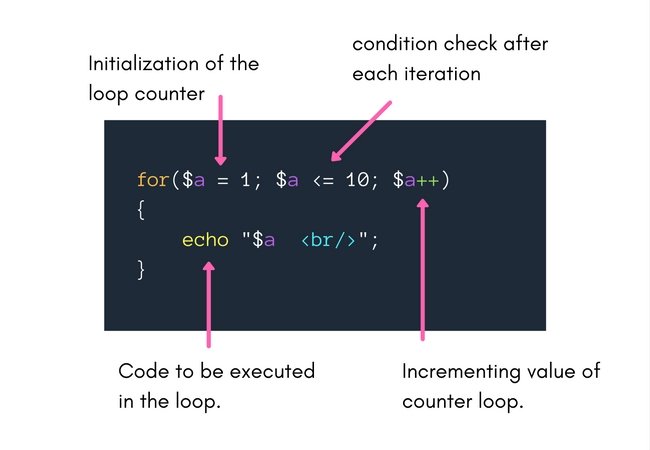
Statements: The code and statements are executed one time in each iteration.ġ0 minutes has 600 seconds Definition of Foreach.Increment: This expression modifies the value of the loop counter and is evaluated in the end of each iteration.If the condition is true the nested statements are executed otherwise the execution will be ceased. Condition: The condition expression is evaluated prior to each iteration.Initialization: The initial values are assigned to the counter variables which is evaluated once unconditionally at the beginning and before the first execution of the body of the loop.The elements of a for loop are given below: The for loops executes a code block again and again until the condition is falsified. While in for loop, the expressions and condition are defined at a time inside the for loop parenthesis as shown in the structure below:įor ( initialization Condition Increment) At last, the counter is modified at the end of each iteration. In the while loop, a counter is set to start with, then it is tested in a condition before each iteration. The key difference between the two is that foreach automatically starts at the front of the array, whereas list()/ each() does not.The for loop is a more concise form of the other loops like while and do while in PHP. In practice, however, you will find foreach loops and list()/ each() loops in about equal proportions, despite the latter option being slower. Generally speaking, using foreach loops is the most optimised way to loop through an array, and is also the easiest to read. There is a lot more detail on array cursors later. The meaning of that first line is "get the current element in the array, and assign its key to $var and its value to $val, then advance the array cursor.
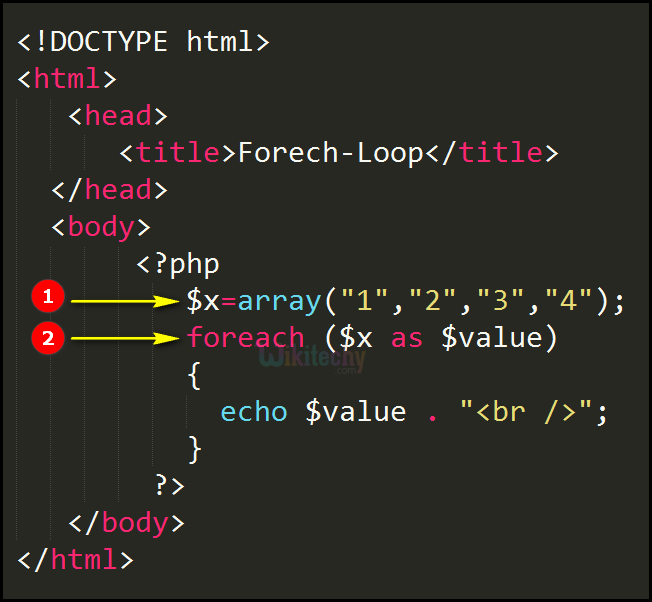
To start with, each() will return the first element, then the second element, then the third, and so on, until it finds there are no elements left, in which case it will return false and end the loop. All arrays have a cursor, and you can freely move it around - it is used in the while loop above, where we need to iterate through an array. "Array cursor" is the technical term for the element of an array that is currently being read. Each() takes an array as its parameter, and returns the current key and value in that array before advancing the array cursor. List() is a function that does the opposite of array() - it takes an array, and converts it into individual variables. The second way to use foreach does allow you to extract keys, and looks like this:Īnother commonly used way to loop over arrays is using the list() and each() functions, like this: In this situation, the array keys are ignored completely, which usually makes most sense when they have been auto-generated (i.e. Here the array $array is looped through and its values are extracted into $val. The easiest way to use foreach looks like this: However, there is a quick and easy way to accomplish the same thing: a foreach loop, which itself has two versions. As a result, code like this should generally be avoided: That is, it can have its keys out of order or entirely missing. For example, an array may have keys 0, 1, 2, 5, 3, 6, 7. However, these numbers cannot be guaranteed to exist within the array in any given order, or even to exist at all - they are just key values themselves. If you do not specify a key, as in the first example, PHP will just assign incrementing numbers starting with 0.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
